In my previous blog we talked about the different languages and notations in the Core Data Services (CDS). In this part today, we will look at what CDS Query Language(CQL) is; how many types of CQL there are, and the basic syntaxes of CQL.
What is SAP CAPM CQL?
CDS Query language(CQL) within the SAP Cloud Application Programming Model (CAPM) is a Standard Query Language (SQL) for connecting to databases. Using SQL you can interact with the database like CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations, for example. It allows you to get the data from database tables using GET call; you can update the existing data in database table records using PATCH call, or insert new records into the database table using POST call. You can also delete records from a table using DELETE call, and perform a variety of other SQL operations.
Firstly, let us begin by exploring what Core Query Notations (CQN) are.
CQN specifications are used to capture queries as plain JavaScript objects. However, by using the query builder APIs you can use respective objects directly in your code.
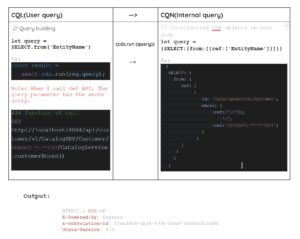
Similarly, as you can see in the example below, I added the user understandable query (select, insert, delete, update) in our code. However, once the query is compiled, it is automatically converted to a capm internal query structure (plain javascript object).

What is a Core Expression Notation (CXN)?
CXN is used to capture expressions as plain JavaScript objects. It is a part of the query that will also convert user expression to expression notation. The queries can be any one of the below.
expr = // one of…
val | // [literal values]: #literal-values
ref | // references or functions
xpr | // operator expressions
func | // function calls
param | // binding parameters
sym | // enum symbol
SELECT // subqueries
let exp = cds.parse.expr

CDS QL is based on standard SQL, which it enhances in different ways :
Using CDS QL you can execute different types of queries. Go about selecting a few columns in the table , joins (LEFT OUTER JOIN), ‘where’ clauses etc.
Postfix Projections : CQL supports the put projections like :
Normal SQL : SELECT name, address.street from Authors;
CQl projection SQL : SELECT from Authors { name, address.street };
It also support “Smart * Selector” like → SELECT from Books { *, author.name as author };
Path Expressions : Use path expressions to navigate along with associations
and/or construct elements in any of the SQL clauses. However, with path expressions in ‘from’ clauses, you can fetch entries from a target entity that associate with a parent entity.
Similarly, path expressions also support all other clauses like ‘where’ clauses, left outer joins, etc.

Casts in CDL : There are two different constructs commonly called casts.
Normal SQL : SELECT cast (foo+1 as Decimal) as bar from Foo;
CDL projection SQL : SELECT from Foo { foo+1 as bar : Decimal };
Excluding Clause: Use the excluding clause in combination with SELECT * to
select all elements except for the ones listed in the exclude list.
Ex: SELECT from Books { * } excluding { author };
Output : In the books table results exclude the author column.
Query-Local Mixins: It is used to mixin localization Associations using mixin
and into a clause.
Ex: SELECT from Books mixin {
localized : Association to LocalizedBooks on localized.ID = ID;
} into {
ID, localized.title
};
Note: Postfix notation only supports this.
If you are interested in viewing similar articles, visit our blog, here.
View our LinkedIn, here.